The Ultimate Guide on Automatic Food Sterilization Insecticide Equipment in 2024
Introduction
Welcome to the ultimate guide on automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment in 2024. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the latest advancements and applications of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment, exploring its importance, working principles, technological innovations, and future outlook. With the growing emphasis on food safety and hygiene, the role of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment has become increasingly vital in ensuring the safety and quality of food products. Join us as we navigate through the intricacies of this essential equipment and uncover its significance in the modern food industry landscape.

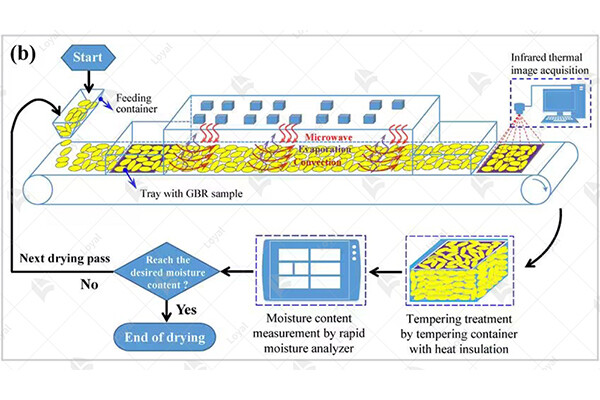
Working principle of automatic food sterilization and pest control equipment
The working principle of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment involves the use of advanced technologies to eliminate harmful microorganisms and pests from food products. These machines typically utilize a combination of heat, pressure, and chemical agents to achieve sterilization and pest control.
High temperatures are employed to kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens present on the surface of food items. This thermal treatment effectively destroys the microorganisms' cell structure, rendering them harmless and preventing foodborne illnesses.
In addition to heat, some automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment may utilize pressure to further enhance the sterilization process. Pressurized steam or water can penetrate deep into food products, ensuring thorough sterilization and eliminating any remaining contaminants.
Furthermore, chemical agents such as insecticides or pesticides may be integrated into the sterilization process to target and eliminate pests, including insects and rodents. These chemicals are carefully selected and applied in precise concentrations to ensure effective pest control without compromising food safety.
Advantages of Automatic Food Sterilization and Pest Control Equipment
1. Enhanced Food Safety |
Automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment utilizes advanced technologies to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and pests from food products, ensuring that they meet stringent safety standards and regulations. |
2. Increased Shelf Life |
By effectively sterilizing food products and eliminating pests, automatic sterilization equipment extends the shelf life of perishable items, reducing food waste and improving overall product quality. |
3. Cost Savings |
Investing in automatic food sterilization and pest control equipment can result in significant cost savings over time by reducing the need for chemical treatments, minimizing product recalls, and preventing damage caused by pests. |
4. Efficiency and Productivity |
Automatic equipment streamlines the sterilization and pest control process, allowing for faster throughput and increased productivity. This improves operational efficiency and ensures timely delivery of safe and high-quality food products to consumers. |
5. Compliance with Regulations |
By employing automatic food sterilization and pest control equipment, food manufacturers can ensure compliance with strict regulatory requirements and industry standards, avoiding fines, penalties, and reputational damage associated with non-compliance. |
6. Versatility |
Automatic sterilization equipment is versatile and can be adapted to different food processing environments and product types, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in various industries, including food production, catering, and food service. |

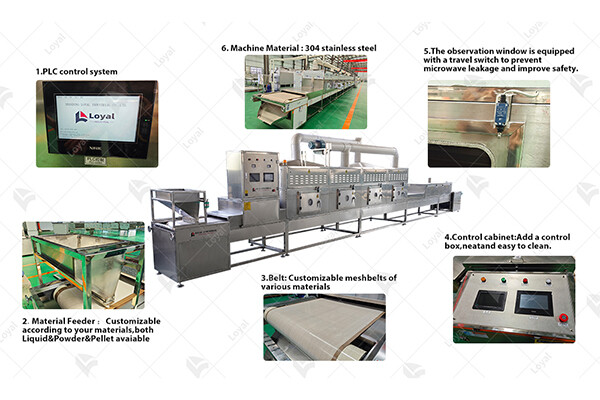
Key Components of Automatic Food Sterilization and Pest Control Equipment
Component | Description |
Microwave Chamber | The microwave chamber is the core component of the automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment. It houses the food products during the sterilization process and provides the necessary environment for microwave treatment. |
Conveyor System | The conveyor system facilitates the movement of food products through the sterilization process. It ensures a continuous flow of products into and out of the microwave chamber, optimizing throughput and efficiency. |
Microwave Generator | The microwave generator is responsible for producing the electromagnetic waves used for sterilization. It generates high-frequency microwaves that penetrate the food products, effectively killing pathogens and pests. |
Pest Control Mechanism | This mechanism is designed to control and eliminate pests within the sterilization equipment. It may include insecticide sprayers, traps, or other pest management devices integrated into the system. |
Temperature and Moisture Sensors | Temperature and moisture sensors monitor the conditions inside the microwave chamber to ensure optimal sterilization effectiveness. They provide real-time data to control the sterilization process and adjust parameters as needed. |
Control Panel | The control panel is the interface used to monitor and manage the operation of the sterilization equipment. It allows operators to set parameters, adjust settings, and monitor performance indicators during the sterilization process. |
Safety Features | Safety features such as interlocks, emergency stop buttons, and alarms are crucial components of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment. They help ensure operator safety and prevent accidents during operation. |
Ventilation System | The ventilation system is responsible for maintaining proper airflow within the microwave chamber and removing excess heat and moisture generated during the sterilization process. It helps prevent overheating and ensures uniform sterilization. |
Cleaning Mechanism | The cleaning mechanism is designed to facilitate the maintenance and sanitation of the equipment. It may include automated cleaning systems or manual cleaning procedures to remove food residues and prevent contamination. |
Data Logging and Reporting | Data logging and reporting functionalities allow operators to track sterilization parameters, record process data, and generate reports for quality control and regulatory compliance purposes. |

Comparison and advantages of microwave technology and traditional sterilization methods
Factors | Microwave Technology | Traditional Sterilization Methods |
Sterilization Process | Utilizes microwave energy to kill pathogens | Relies on heat, pressure, or chemicals |
Speed | Rapid sterilization process | May require longer processing times |
Energy Efficiency | Generally more energy-efficient | May consume more energy |
Quality of Sterilization | Even and thorough sterilization | Potential for uneven results |
Preservation of Nutrients | Minimal nutrient loss | May result in nutrient degradation |
Environmental Impact | Lower environmental footprint | Potential for chemical waste |
Equipment Cost | Initial investment may be higher | Lower initial investment |
Operational Complexity | Requires specialized equipment and training | May be simpler to operate |
Technical parameters
| Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine | |||||
| Model | Size LWH(Can be customized according to the customer's requirements) | Output power | Dewaterability | Sterilization capacity | Baking and Roasting capacity (Depends on different raw material) |
| LY-10KW | 5000mm825mm1750mm | ≥10KW | 10KG/Hour | 100KG/Hour | 30-50KG/Hour |
| LY-20KW | 8000mm825mm1750mm | ≥20KW | 20KG/Hour | 200KG/Hour | 60-100KG/Hour |
| LY-30KW | 8500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥30KW | 30KG/Hour | 300KG/Hour | 90-150 KG/Hour |
| LY-40KW | 10000mm1160mm1750mm | ≥40KW | 40KG/Hour | 40KG/Hour | 120-200KG/Hour |
| LY-50KW | 12500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥50KW | 50KG/Hour | 500KG/Hour | 150-250KG/Hour |
| LY-60KW | 13500mm1450mm1750mm | ≥60KW | 60KG/Hour | 600KG/Hour | 180-300KG/Hour |
| LY-70KW | 13500mm1500mm1750mm | ≥70KW | 70KG/Hour | 700KG/Hour | 210-350KG/Hour |
| LY-80KW | 13500mm1650mm1750mm | ≥80KW | 80KG/Hour | 800KG/Hour | 240-400KG/Hour |
| LY-100KW | 16800mm1650mm1750mm | ≥100KW | 100KG/Hour | 1000KG/Hour | 300-500KG/Hour |
| LY-150KW | 22400mm1850mm1750mm | ≥150KW | 150KG/Hour | 1500KG/Hour | 450-750KG/Hour |
| LY-200KW | 27000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥250KW | 250KG/Hour | 2500KG/Hour | 750-1250/Hour |
| LY-300KW | 32000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥300KW | 300KG/Hour | 3000KG/Hour | 900-1500KG/Hour |
| Power Supply | 380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire | ||||
| Microwave Output Frequency | 2450±50Mhz | ||||
| Microwave Input Apparent Power | ≤168Kva | ||||
| Microwave Output Power | ≥120Kw | ||||
| Microwave Power Adjustment Range | 0-30Kw(Adjustable) | ||||
| Ambient Temperature | -5-40°C | ||||
| Relative Humidity | ≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas | ||||
| Transmission Speed | 0-10m/Min(Adjustable) | ||||

Application of Automatic Food Sterilization and Pest Control Equipment
Automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment plays a pivotal role in ensuring food safety and quality by effectively eliminating harmful microorganisms and pests from food processing environments. In 2024, the application of this advanced equipment continues to evolve, offering innovative solutions to address various challenges in the food industry.
1. Food Processing Facilities:
One of the primary applications of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment is in food processing facilities. These facilities handle large volumes of raw ingredients and finished products, making them susceptible to contamination by bacteria, viruses, and insects. By installing automatic sterilization equipment, food manufacturers can maintain a hygienic environment and prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses.
2. Packaging and Storage Areas:
Packaging and storage areas are critical points in the food supply chain where contamination can occur. Automatic sterilization equipment installed in these areas helps eliminate pathogens and pests that may come into contact with food products during packaging and storage. This proactive approach ensures that the integrity and safety of the food products are preserved throughout the distribution process.
3. Transportation Vehicles:
Transportation vehicles, such as trucks and containers, play a vital role in transporting food products from production facilities to distribution centers and retail outlets. Automatic sterilization equipment installed in these vehicles helps prevent cross-contamination and maintains the cleanliness of the transportation environment. By ensuring that vehicles are free from pests and pathogens, food safety risks during transit are minimized.
4. Retail and Hospitality Establishments:
Retail stores, restaurants, and hospitality establishments also benefit from the application of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment. These environments are frequented by large numbers of people, increasing the risk of contamination and pest infestations. By implementing automatic sterilization measures, businesses can uphold hygiene standards and protect the health of their customers.
5. Agricultural and Farming Operations:
In agricultural and farming operations, automatic sterilization equipment is used to sanitize equipment, tools, and facilities to prevent the spread of diseases and pests among crops and livestock. By maintaining a clean and pest-free environment, farmers can improve crop yields, reduce crop losses, and ensure the quality of agricultural products.

Technological Progress and Innovation of Automatic Food Sterilization and Pest Control Equipment
1. Integration of Advanced Sensors and AI:
Modern automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment now incorporates advanced sensors and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to enhance efficacy and precision. These sensors detect contaminants and pests with unparalleled accuracy, allowing for targeted and efficient sterilization and pest control measures.
2. IoT Connectivity and Remote Monitoring:
The advent of Internet of Things (IoT) technology has enabled seamless connectivity and remote monitoring capabilities in automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment. Operators can now remotely monitor equipment performance, receive real-time alerts, and even adjust settings remotely, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
3. Enhanced Sterilization Techniques:
New sterilization techniques have emerged, leveraging technologies such as ozone generation, ultraviolet (UV) light, and cold plasma to achieve superior sterilization results. These techniques offer alternatives to traditional methods, providing more environmentally friendly and residue-free sterilization solutions.
4. Eco-Friendly Pest Control Solutions:
In response to growing environmental concerns, manufacturers have developed eco-friendly pest control solutions integrated into automatic food sterilization equipment. These solutions utilize non-toxic substances or biological agents to repel or eliminate pests while ensuring food safety and quality.
5. Smart Pest Detection and Management:
Automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment now features smart pest detection and management capabilities, allowing for proactive pest monitoring and control. AI algorithms analyze data from sensors and cameras to identify pest hotspots and deploy targeted pest control measures, minimizing the risk of infestation.
6. Modular and Scalable Designs:
Manufacturers have introduced modular and scalable designs in automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment, allowing for customization and flexibility to meet the diverse needs of food processing facilities. These designs facilitate easy integration into existing production lines and enable seamless scalability as production volumes fluctuate.
7. Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
As food safety regulations continue to evolve, automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment is designed to comply with stringent regulatory standards and certifications. Manufacturers prioritize the development of equipment that meets or exceeds industry regulations, ensuring compliance and consumer confidence in food safety.

Challenges and Limitations of Automatic Food Sterilization and Pest Control Equipment
Automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety by eliminating harmful pathogens and pests from food products. However, like any technology, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing the effectiveness of the equipment and addressing potential drawbacks.
1. Effectiveness Against Resistant Pathogens:
One of the primary challenges faced by automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment is its effectiveness against resistant pathogens. Some microorganisms may develop resistance to conventional sterilization methods, rendering them less effective in eliminating harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi from food products.
2. Residual Effects and Chemical Residues:
While automatic sterilization and pest control equipment are designed to eliminate pests and pathogens, there may be concerns regarding residual effects and chemical residues left behind on food products. Excessive use of insecticides and sterilizing agents may lead to the accumulation of harmful residues, posing risks to human health and food safety.
3. Environmental Impact:
Another limitation of automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment is its potential environmental impact. Chemical insecticides and sterilizing agents may contaminate soil, water, and air, leading to adverse effects on ecosystems and non-target organisms. Additionally, the use of certain chemicals may contribute to the development of pesticide-resistant pests, exacerbating pest control challenges in the long run.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards:
Compliance with regulatory requirements and safety standards is paramount when using automatic food sterilization insecticide equipment. Manufacturers and operators must adhere to strict guidelines regarding the use of chemicals and ensure that equipment is properly maintained and calibrated to prevent overuse or misuse, which could result in health and safety hazards.
5. Cost Considerations:
Investing in automatic food sterilization and pest control equipment can involve significant upfront costs, including equipment purchase, installation, and training. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and replacement of consumables such as insecticides and sterilizing agents incur additional expenses. For some businesses, especially small-scale producers, these costs may pose a barrier to adoption.

Post-maintenance of Automatic Food Sterilization Insecticide Equipment
1. Inspection and Testing:
Following maintenance, thorough inspection and testing are essential to verify that all components are functioning correctly. This includes checking the integrity of seals, verifying the accuracy of temperature and pressure gauges, and ensuring proper calibration of sensors.
2. Cleaning and Sanitization:
Cleaning and sanitizing the equipment are critical steps to prevent contamination and maintain hygiene standards. All surfaces that come into contact with food products should be thoroughly cleaned using approved sanitizing agents to eliminate any microbial contaminants.
3. Lubrication and Component Check:
Moving parts and components should be adequately lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Additionally, all mechanical and electrical components should be checked for signs of wear or damage and replaced if necessary to prevent unexpected breakdowns during operation.
4. Calibration and Adjustment:
Calibrating the equipment's sterilization and insecticide functions is essential to ensure effective treatment of food products. Proper calibration ensures that the sterilization and insecticide processes achieve the desired levels of efficacy while minimizing any potential adverse effects on food quality.
5. Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintaining comprehensive documentation of all maintenance activities is crucial for regulatory compliance and quality assurance purposes. Records should include details of the maintenance performed, any repairs or replacements made, and the results of inspection and testing procedures.
6. Training and Education:
Providing ongoing training and education to operators and maintenance personnel is vital for ensuring proper operation and maintenance of the equipment. Training programs should cover safety protocols, equipment operation procedures, and troubleshooting techniques to empower personnel to handle any issues that may arise effectively.

References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of industrial microwaves:
1. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
Website: [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/]
2.ScienceDirect
Website: [https://www.sciencedirect.com/]
3. SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4. Wiley Online Library
Website: [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/]
5. PubMed
Website: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/]
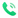 Telephone :+86-531-55583139
Telephone :+86-531-55583139 WhatsApp :+86 13256674591
WhatsApp :+86 13256674591 Email :
Email :