The Ultimate Guide to Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machine in 2024
Introduction
In 2024, the use of advanced technology in food processing has become increasingly prevalent, particularly in the preservation of food products. One such innovation is the Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machine, which has revolutionized the way preserved foods are sterilized and preserved. This guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into the functionality, benefits, and applications of the Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machine in 2024. By understanding the capabilities of this cutting-edge technology, food manufacturers can ensure the safety, quality, and longevity of preserved food products, meeting the demands of consumers and regulatory standards alike.

Working principle of microwave sterilizer
The working principle of a Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machine is rooted in the application of microwave technology to eliminate harmful microorganisms while maintaining the quality of preserved food products.
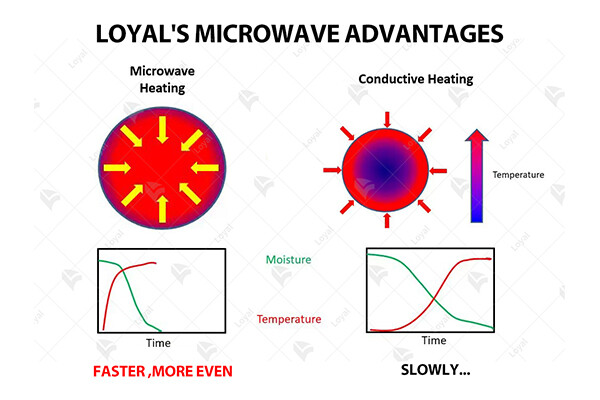
Microwave sterilization works by exposing the preserved food products to microwave radiation, which penetrates the food and disrupts the cellular structure of any microorganisms present. This process effectively deactivates bacteria, viruses, and fungi, ensuring the safety and shelf-life of the preserved foods. Unlike traditional sterilization methods such as heat pasteurization, microwave sterilization offers rapid and uniform heating, minimizing nutrient loss and preserving the natural taste and texture of the food products.
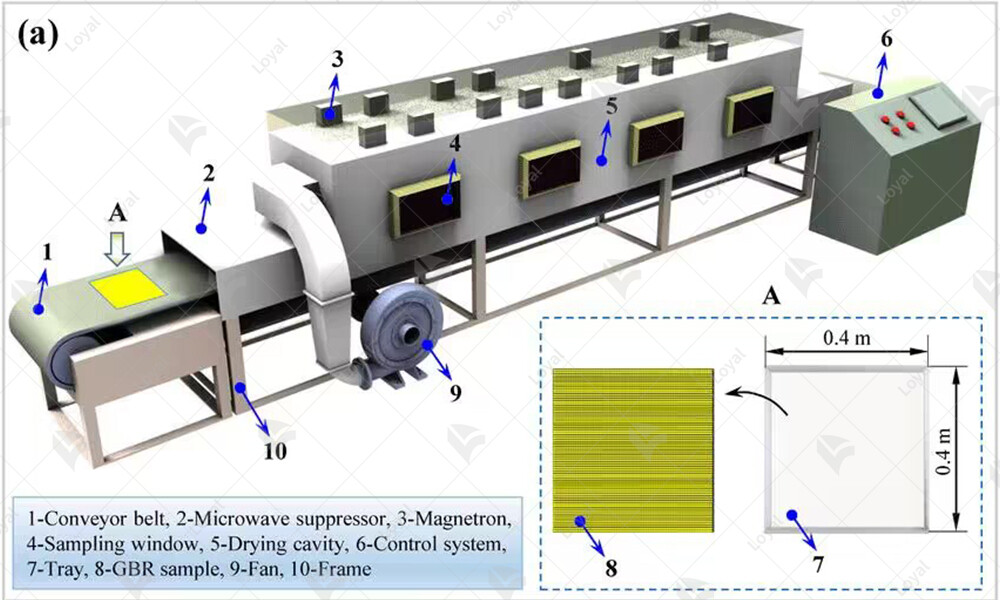
The microwave sterilization machine consists of a chamber where the preserved food products are placed on a conveyor belt or tray. Microwave generators emit electromagnetic waves into the chamber, creating a field of intense energy that heats the food products from the inside out. Temperature and power settings are carefully controlled to achieve the desired level of sterilization without overheating or damaging the food. Additionally, the machine may incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor and adjust the sterilization process in real-time, ensuring consistent results batch after batch.
Advantages of microwave sterilizer
Advantages of Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machine |
1. Rapid Sterilization:Microwave technology allows for rapid heating of food products, resulting in quick sterilization and reduced processing time. |
2. Uniform Heating:The microwave sterilizer ensures uniform heating throughout the food product, eliminating cold spots and ensuring thorough sterilization. |
3. Preservation of Nutritional Value:Unlike traditional sterilization methods, microwave sterilization preserves the nutritional value, flavor, and texture of preserved foods, maintaining their quality and integrity. |
4. Energy Efficiency:Microwave sterilization requires less energy compared to conventional methods such as thermal processing, making it a more energy-efficient option for food processing operations. |
5. Minimal Chemical Usage:Microwave sterilization does not require the use of chemical additives or preservatives, reducing the risk of chemical residues in preserved foods and ensuring product safety. |
6. Versatility:The Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machine is versatile and can be used for a wide range of food products, including fruits, vegetables, meat, and seafood, offering flexibility in food processing operations. |
7. Reduced Microbial Load:Microwave sterilization effectively reduces the microbial load in preserved foods, extending their shelf life and enhancing food safety. |
8. Automation and Control:Modern microwave sterilizers are equipped with advanced automation and control systems, allowing for precise adjustment of sterilization parameters and ensuring consistent product quality. |
Comparison and advantages of microwave technology and traditional sterilization methods
Aspect | Microwave Sterilization | Traditional Sterilization |
Speed | Rapid heating process | Longer processing time |
Efficiency | Highly efficient | May require multiple cycles |
Temperature Control | Precise temperature control | Limited control over temperature |
Preservation of Nutrients | Preserves nutrients due to shorter processing time | May result in nutrient loss due to prolonged heat exposure |
Energy Consumption | Lower energy consumption | Higher energy consumption |
Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint | May involve the use of chemicals with environmental impact |
Uniformity | Provides uniform heating throughout the product | May result in uneven heating, leading to inconsistent sterilization |
Safety | Ensures safe and thorough sterilization | May pose safety risks due to handling of chemicals or high temperatures |
Types of microwave sterilizers
Types of microwave sterilizers vary depending on the specific needs and requirements of the preserved food industry in 2024. These machines are designed to utilize microwave technology for effectively and efficiently sterilizing preserved food products, ensuring their safety and prolonging their shelf life. Here are some common types of microwave sterilizers:
1. Batch Microwave Sterilizers:
Batch microwave sterilizers are designed to process preserved food products in discrete batches. They typically consist of a chamber where the food products are loaded onto trays or racks and subjected to microwave radiation for sterilization. Batch sterilizers are suitable for small to medium-scale production and offer flexibility in processing different types of preserved foods.
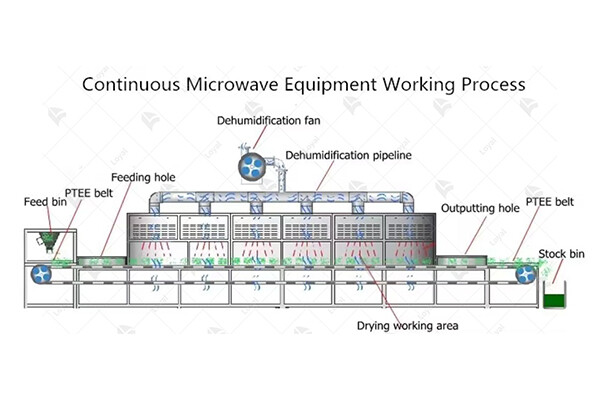
2. Continuous Microwave Sterilization Systems:
Continuous microwave sterilization systems are designed for high-volume production of preserved food products. These systems feature a continuous conveyor belt or other mechanisms for continuously feeding the food products through the sterilization chamber. Continuous sterilizers offer high throughput and efficiency, making them ideal for large-scale production facilities.
3. Tunnel Microwave Sterilization Systems:
Tunnel microwave sterilization systems are a specialized type of continuous sterilizer designed for specific applications. They feature a tunnel-like structure with a conveyor belt running through the length of the tunnel. Preserved food products are fed into one end of the tunnel and transported through the chamber, where they are subjected to microwave radiation for sterilization. Tunnel sterilizers are commonly used for products that require precise control over temperature and processing time.
4. Combination Microwave and Hot Air Sterilization Systems:
Combination microwave and hot air sterilization systems combine microwave technology with hot air convection for enhanced sterilization performance. These systems utilize both microwave radiation and hot air circulation to achieve thorough sterilization of preserved food products. They are particularly effective for products that require a combination of heat and moisture to achieve sterilization.
5. Customized Microwave Sterilization Solutions:
In addition to standard types of microwave sterilizers, customized solutions are available to meet specific needs and requirements. Manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of microwave sterilization systems to accommodate unique product characteristics, processing parameters, and production volumes.
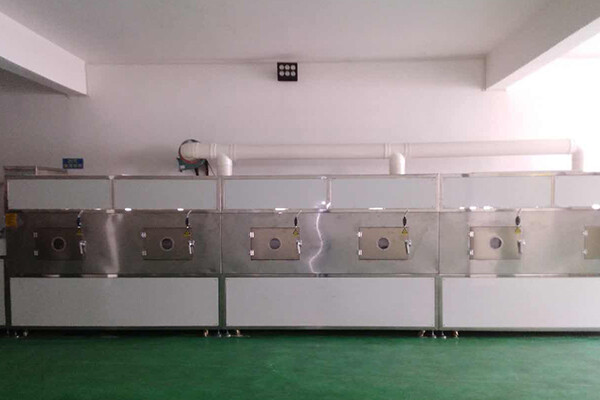

Technical parameters
| Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine | |||||
| Model | Size LWH(Can be customized according to the customer's requirements) | Output power | Dewaterability | Sterilization capacity | Baking and Roasting capacity (Depends on different raw material) |
| LY-10KW | 5000mm825mm1750mm | ≥10KW | 10KG/Hour | 100KG/Hour | 30-50KG/Hour |
| LY-20KW | 8000mm825mm1750mm | ≥20KW | 20KG/Hour | 200KG/Hour | 60-100KG/Hour |
| LY-30KW | 8500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥30KW | 30KG/Hour | 300KG/Hour | 90-150 KG/Hour |
| LY-40KW | 10000mm1160mm1750mm | ≥40KW | 40KG/Hour | 40KG/Hour | 120-200KG/Hour |
| LY-50KW | 12500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥50KW | 50KG/Hour | 500KG/Hour | 150-250KG/Hour |
| LY-60KW | 13500mm1450mm1750mm | ≥60KW | 60KG/Hour | 600KG/Hour | 180-300KG/Hour |
| LY-70KW | 13500mm1500mm1750mm | ≥70KW | 70KG/Hour | 700KG/Hour | 210-350KG/Hour |
| LY-80KW | 13500mm1650mm1750mm | ≥80KW | 80KG/Hour | 800KG/Hour | 240-400KG/Hour |
| LY-100KW | 16800mm1650mm1750mm | ≥100KW | 100KG/Hour | 1000KG/Hour | 300-500KG/Hour |
| LY-150KW | 22400mm1850mm1750mm | ≥150KW | 150KG/Hour | 1500KG/Hour | 450-750KG/Hour |
| LY-200KW | 27000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥250KW | 250KG/Hour | 2500KG/Hour | 750-1250/Hour |
| LY-300KW | 32000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥300KW | 300KG/Hour | 3000KG/Hour | 900-1500KG/Hour |
| Power Supply | 380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire | ||||
| Microwave Output Frequency | 2450±50Mhz | ||||
| Microwave Input Apparent Power | ≤168Kva | ||||
| Microwave Output Power | ≥120Kw | ||||
| Microwave Power Adjustment Range | 0-30Kw(Adjustable) | ||||
| Ambient Temperature | -5-40°C | ||||
| Relative Humidity | ≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas | ||||
| Transmission Speed | 0-10m/Min(Adjustable) | ||||
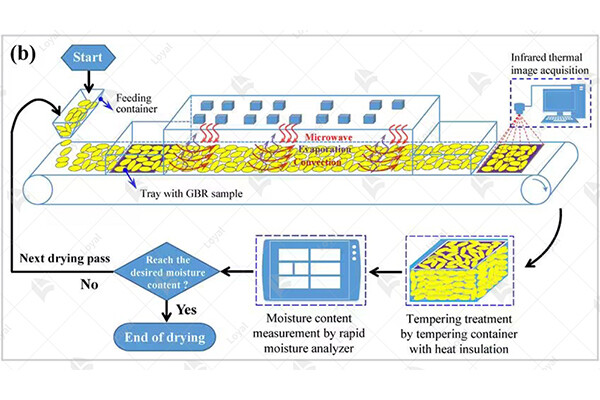
Technological progress and innovation of microwave sterilizers
Types of microwave sterilizers vary depending on the specific needs and requirements of the preserved food industry in 2024. These machines are designed to utilize microwave technology for effectively and efficiently sterilizing preserved food products, ensuring their safety and prolonging their shelf life. Here are some common types of microwave sterilizers:
1. Batch Microwave Sterilizers:
Batch microwave sterilizers are designed to process preserved food products in discrete batches. They typically consist of a chamber where the food products are loaded onto trays or racks and subjected to microwave radiation for sterilization. Batch sterilizers are suitable for small to medium-scale production and offer flexibility in processing different types of preserved foods.
2. Continuous Microwave Sterilization Systems:
Continuous microwave sterilization systems are designed for high-volume production of preserved food products. These systems feature a continuous conveyor belt or other mechanisms for continuously feeding the food products through the sterilization chamber. Continuous sterilizers offer high throughput and efficiency, making them ideal for large-scale production facilities.
3. Tunnel Microwave Sterilization Systems:
Tunnel microwave sterilization systems are a specialized type of continuous sterilizer designed for specific applications. They feature a tunnel-like structure with a conveyor belt running through the length of the tunnel. Preserved food products are fed into one end of the tunnel and transported through the chamber, where they are subjected to microwave radiation for sterilization. Tunnel sterilizers are commonly used for products that require precise control over temperature and processing time.
4. Combination Microwave and Hot Air Sterilization Systems:
Combination microwave and hot air sterilization systems combine microwave technology with hot air convection for enhanced sterilization performance. These systems utilize both microwave radiation and hot air circulation to achieve thorough sterilization of preserved food products. They are particularly effective for products that require a combination of heat and moisture to achieve sterilization.
5. Customized Microwave Sterilization Solutions:
In addition to standard types of microwave sterilizers, customized solutions are available to meet specific needs and requirements. Manufacturers can tailor the design and specifications of microwave sterilization systems to accommodate unique product characteristics, processing parameters, and production volumes.

Technological progress and innovation of microwave sterilizers
In 2024, the technological progress and innovation of microwave sterilizers have significantly advanced the field of food preservation, particularly in the context of preserved foods. Microwave sterilizers have undergone continuous refinement and enhancement to meet the evolving needs of the food industry, ensuring both efficiency and effectiveness in the sterilization process.
Advancements in Microwave Technology:
One of the key areas of innovation in microwave sterilizers is the advancement of microwave technology itself. Manufacturers have developed more sophisticated microwave generators and applicators, allowing for greater control over the sterilization process. This enables precise adjustment of power levels, frequencies, and exposure times to achieve optimal results for various types of preserved foods.
Integration of Smart Features:
Another notable development is the integration of smart features into microwave sterilizers. These smart features may include sensor technology for real-time monitoring of temperature and humidity levels, as well as automation capabilities for adjusting sterilization parameters based on product characteristics. Such advancements enhance efficiency, reduce human error, and ensure consistent sterilization outcomes.
Enhanced Safety Measures:
Safety remains a paramount concern in the design of microwave sterilization machines. Manufacturers have implemented enhanced safety measures to mitigate risks associated with microwave radiation and high temperatures. This includes the incorporation of safety interlocks, protective shielding, and comprehensive user training protocols to minimize the potential for accidents and ensure operator safety.
Improved Energy Efficiency:
Efforts have also been made to improve the energy efficiency of microwave sterilizers. By optimizing heating patterns and minimizing energy loss, manufacturers have succeeded in reducing the overall energy consumption of these machines while maintaining high levels of sterilization efficacy. This not only reduces operating costs but also aligns with sustainability objectives.
Customization and Adaptability:
Modern microwave sterilizers are increasingly designed to be customizable and adaptable to different production environments and product requirements. They offer flexibility in terms of batch sizes, processing times, and sterilization conditions, allowing food manufacturers to tailor the sterilization process to their specific needs and preferences.
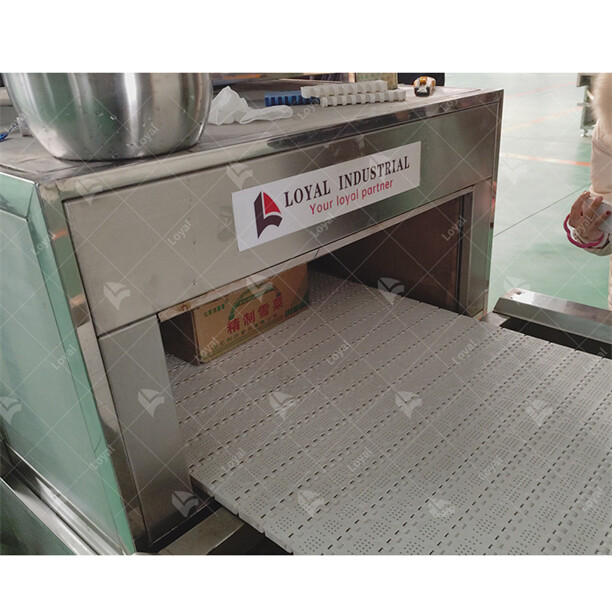

Precautions for selection and implementation of microwave sterilizers
When selecting and implementing Preserved Food Microwave Sterilization Machines, certain precautions must be considered to ensure optimal performance and food safety standards.
1. Understanding Product Requirements:
Before choosing a microwave sterilizer, it's essential to understand the specific requirements of the preserved food products you'll be processing. Consider factors such as product type, packaging materials, required throughput, and desired sterilization levels.
2. Evaluating Sterilization Technology:
Carefully evaluate the sterilization technology offered by different microwave sterilizer manufacturers. Look for advanced features such as precise temperature and power control, uniform distribution of microwave energy, and integrated monitoring systems for accurate sterilization.
3. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
Ensure that the selected microwave sterilizer complies with relevant food safety regulations and industry standards. Verify certifications and accreditations, such as FDA approval, CE marking, and ISO compliance, to guarantee the equipment meets regulatory requirements.
4. Assessing Equipment Reliability:
Choose a microwave sterilization machine from a reputable manufacturer known for producing reliable and durable equipment. Evaluate factors such as build quality, component reliability, and serviceability to minimize the risk of downtime and maintenance issues.
5. Conducting Pilot Testing:
Before full-scale implementation, conduct pilot testing with the selected microwave sterilizer to assess its performance with your specific preserved food products. Evaluate sterilization effectiveness, product quality, and throughput to identify any potential challenges or adjustments needed.
6. Training and Education:
Provide comprehensive training for operators and maintenance personnel on the proper use and maintenance of the microwave sterilization machine. Ensure that staff members understand operating procedures, safety protocols, and troubleshooting techniques to optimize machine performance.
7. Developing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
Develop detailed SOPs for the operation, maintenance, and cleaning of the microwave sterilizer. Document step-by-step procedures, safety precautions, and quality control measures to ensure consistency and adherence to best practices.
8. Establishing Monitoring and Quality Assurance Protocols:
Implement robust monitoring and quality assurance protocols to ensure the effectiveness of the sterilization process and the safety of preserved food products. Monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and microbial load regularly and conduct periodic validation tests to verify sterilization efficacy.

Post-maintenance of microwave sterilizers
Post-maintenance of microwave sterilizers is a critical aspect of ensuring their optimal functionality and effectiveness in sterilizing preserved food. Proper maintenance procedures help to prolong the lifespan of the sterilization equipment and maintain the highest standards of food safety and quality.
1. Cleaning and Sanitization:
After each use, thoroughly clean and sanitize all components of the microwave sterilization machine. This includes the chamber, conveyor belts, trays, and any other surfaces that come into contact with the preserved food. Use approved cleaning agents and follow manufacturer guidelines to eliminate any traces of contaminants and bacteria.
2. Inspection of Components:
Regularly inspect all components of the microwave sterilizer for signs of wear and tear. Check seals, gaskets, and electrical connections to ensure they are intact and functioning properly. Replace any damaged or worn-out parts promptly to prevent leakage or malfunction during operation.
3. Calibration and Adjustment:
Periodically calibrate the microwave sterilization machine according to manufacturer specifications. This involves adjusting power levels, temperature settings, and conveyor speed to ensure consistent and effective sterilization of preserved food. Use calibrated instruments and follow standard procedures to achieve accurate results.
4. Testing and Validation:
Conduct regular testing and validation procedures to verify the performance of the microwave sterilizer. Run test cycles with controlled parameters and monitor the sterilization process closely. Validate the effectiveness of the sterilization by testing samples of preserved food for microbial load and quality attributes.
5. Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities and testing results. Document cleaning schedules, component inspections, calibration adjustments, and validation tests. Keep comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance with food safety regulations and quality assurance standards.
6. Training and Education:
Provide training for operators and maintenance personnel on proper post-maintenance procedures. Ensure that staff members are familiar with the operation of the microwave sterilizer and understand their responsibilities in maintaining its functionality and cleanliness. Continuous education and training are essential for upholding food safety standards and optimizing machine performance.
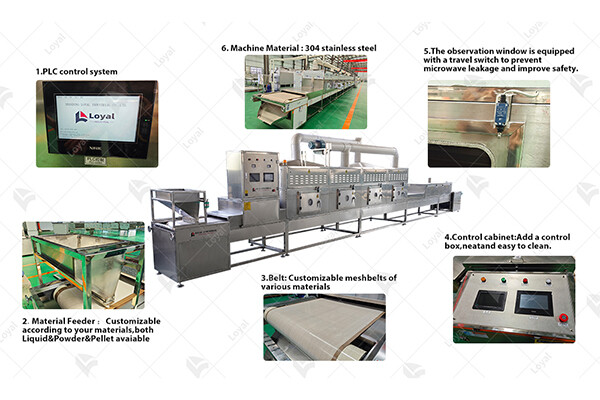

References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of industrial microwaves:
1. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
Website: [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/]
2.ScienceDirect
Website: [https://www.sciencedirect.com/]
3. SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4. Wiley Online Library
Website: [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/]
5. PubMed
Website: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/]
 Telephone :+86-531-55583139
Telephone :+86-531-55583139 WhatsApp :+86 13256674591
WhatsApp :+86 13256674591 Email :
Email :