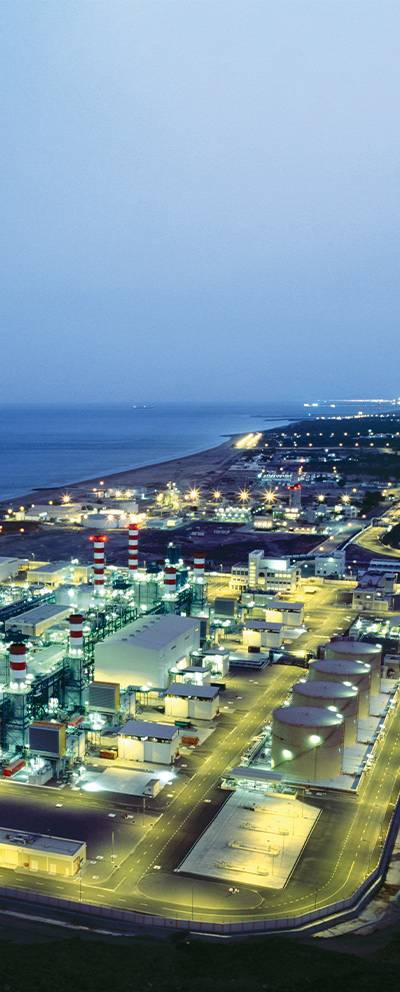
Everything you need to know about sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machine in 2024
Introduction
In 2024, sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines stand at the forefront of innovation in food processing technology. These advanced machines utilize microwave technology to effectively sterilize sauces, ensuring their safety and prolonging their shelf life. As the demand for safe and high-quality food products continues to rise, understanding the capabilities and benefits of sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines is essential for manufacturers in the food industry. In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about these machines, including their operational mechanism, advantages, applications, maintenance, and future trends. Let's delve into the details of how sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines are revolutionizing the food processing industry in 2024 and beyond.
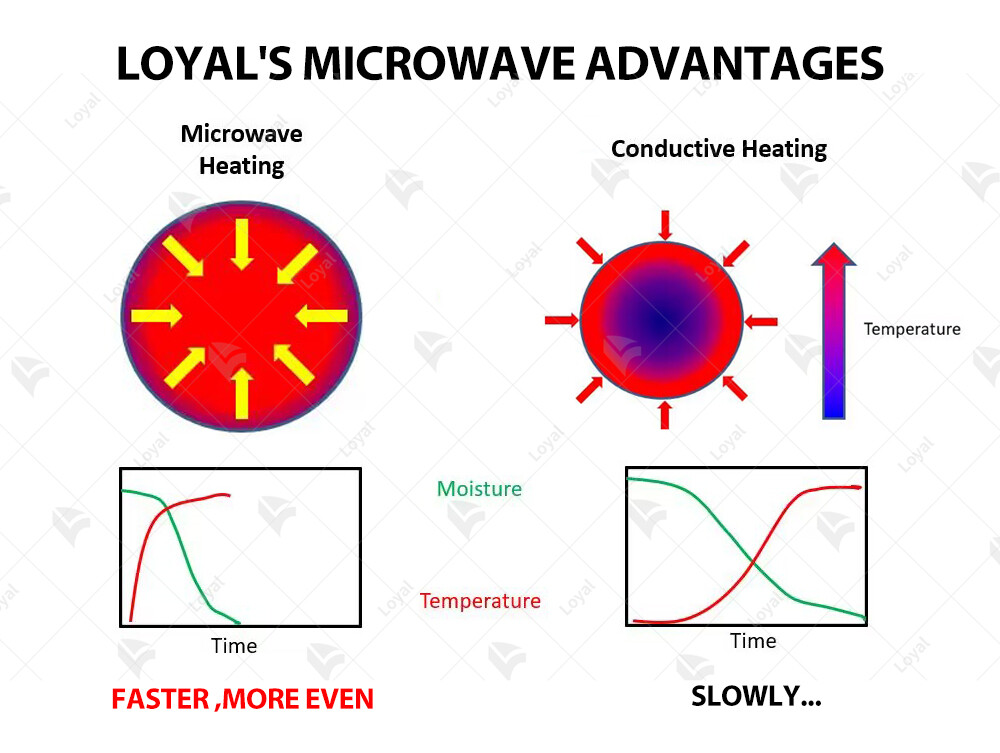
Working principle of microwave sterilizer
The working principle of a sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machine involves the utilization of microwave radiation to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms in sauces while preserving their flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
Microwave Radiation:
Microwave sterilization relies on the application of electromagnetic radiation at specific frequencies to heat the sauces evenly throughout the product. This radiation penetrates the sauces, causing water molecules to vibrate and generate heat rapidly. As a result, the temperature within the sauces increases, leading to the destruction of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
Uniform Heating:
One of the key aspects of the working principle is the ability of microwave radiation to ensure uniform heating of sauces. Unlike conventional sterilization methods that rely on external heat sources, such as steam or hot water, microwave sterilization heats the sauces from within. This uniform heating helps to achieve consistent sterilization across the entire volume of sauces, minimizing the risk of under-processing or over-processing.
Short Processing Time:
Another characteristic of microwave sterilization is its short processing time. Compared to traditional sterilization methods, which may require prolonged exposure to high temperatures, microwave sterilization can achieve the same level of microbial reduction in a fraction of the time. This rapid processing helps to preserve the color, flavor, and nutritional quality of sauces, making them more appealing to consumers.
Preservation of Nutritional Value:
Microwave sterilization is renowned for its ability to preserve the nutritional value of food products, including sauces. By minimizing the exposure of sauces to prolonged heat, microwave sterilization helps to retain vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. This ensures that the sterilized sauces remain nutritious and beneficial for consumers' health.
Safety and Efficiency:
Overall, the working principle of a sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machine prioritizes safety and efficiency. By harnessing the power of microwave radiation, this technology provides a fast, effective, and environmentally friendly method for sterilizing sauces while maintaining their quality. In 2024 and beyond, microwave sterilization machines continue to play a vital role in ensuring the safety and integrity of sauces for consumers worldwide.
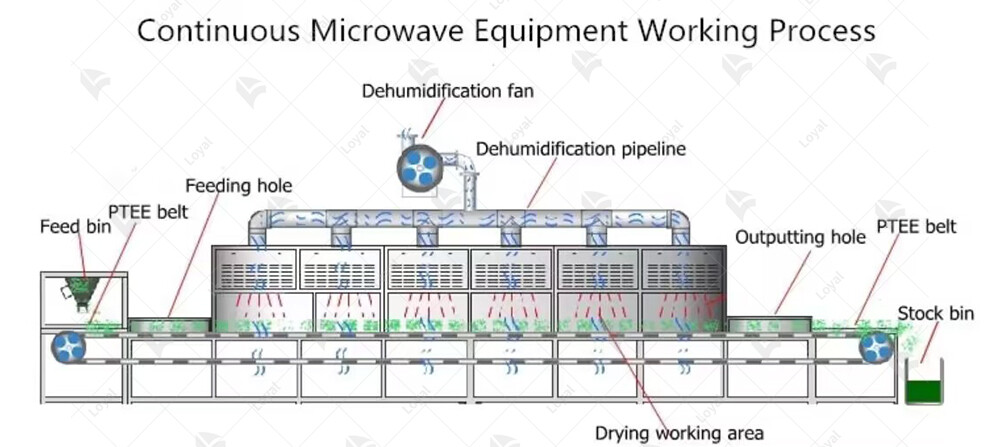
Key components of microwave sterilizer for sauces
Component | Description |
Microwave Generator | Produces microwave radiation used for sterilization process. |
Tunnel Chamber | Enclosed space where sauces are placed on conveyor belts for sterilization. |
Conveyor System | Transports sauces through the tunnel chamber at a controlled speed for uniform sterilization. |
Microwave Source | Emits microwave radiation into the chamber, ensuring even distribution and penetration of heat. |
Temperature Sensor | Monitors and regulates the temperature inside the chamber to maintain optimal sterilization conditions. |
Humidity Control | Regulates the humidity level within the chamber to prevent overdrying or excessive moisture retention. |
Safety Interlocks | Ensures the microwave sterilizer operates safely by preventing access to the chamber during operation. |
Control Panel | Allows operators to set and adjust sterilization parameters such as time, temperature, and power level. |
Cooling System | Prevents overheating of components and maintains a stable operating temperature for prolonged use. |
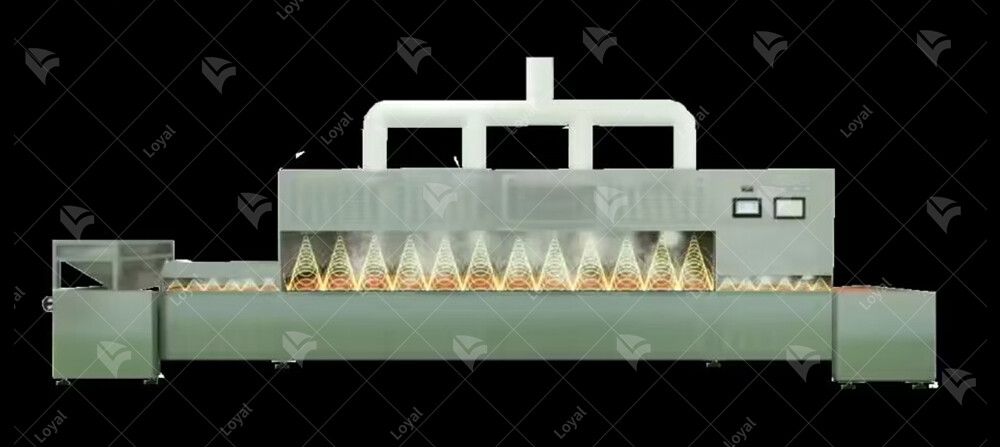

Comparison and advantages of microwave technology and traditional sterilization methods
Criteria | Microwave Sterilization Machine | Traditional Sterilization Methods |
Sterilization Time | Short | Longer |
Temperature Control | Precise | Less precise |
Energy Consumption | Lower | Higher |
Preservation of Nutritional Value | Better | Less effective |
Uniformity of Sterilization | High | Variable |
Equipment Footprint | Compact | Larger |
Labor Intensity | Lower | Higher |
Overall Efficiency | Higher | Lower |

Types of microwave sterilizers
In 2024, various types of microwave sterilizers are available to meet the diverse needs of the food industry, including sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines. These machines are specifically designed for sterilizing sauces and other liquid or semi-liquid products efficiently and effectively using microwave technology.
1. Tunnel Type Microwave Sterilization Machine:
Tunnel type microwave sterilization machines are conveyor belt-based systems that pass products through a tunnel-like chamber where they are exposed to controlled microwave radiation. These machines are ideal for high-volume production and can sterilize sauces rapidly and uniformly. They offer precise temperature and power control, ensuring consistent results and preserving the quality of sauces.
2. Batch Microwave Sterilization Machine:
Batch microwave sterilization machines process sauces in discrete batches, allowing for more flexibility in production schedules and product variations. These machines are well-suited for smaller-scale operations or for processing specialty sauces with unique requirements. They offer customizable settings and are often used for research and development purposes.
3. Continuous Flow Microwave Sterilization System:
Continuous flow microwave sterilization systems provide a continuous processing flow for sauces, eliminating the need for batch processing and reducing production downtime. These systems utilize a continuous conveyor belt or pump to continuously feed sauces through the sterilization chamber, resulting in high throughput and efficiency. They are commonly used in large-scale production facilities.
4. Hybrid Microwave-Convective Sterilization System:
Hybrid microwave-convective sterilization systems combine microwave and convection heating technologies to achieve optimal sterilization results for sauces. These systems utilize a combination of microwave radiation and hot air convection to penetrate and uniformly heat the sauces, ensuring thorough sterilization while minimizing quality degradation. They are particularly suitable for heat-sensitive sauces that require gentle processing.

Technical parameters
| Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine | |||||
| Model | Size LWH(Can be customized according to the customer's requirements) | Output power | Dewaterability | Sterilization capacity | Baking and Roasting capacity (Depends on different raw material) |
| LY-10KW | 5000mm825mm1750mm | ≥10KW | 10KG/Hour | 100KG/Hour | 30-50KG/Hour |
| LY-20KW | 8000mm825mm1750mm | ≥20KW | 20KG/Hour | 200KG/Hour | 60-100KG/Hour |
| LY-30KW | 8500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥30KW | 30KG/Hour | 300KG/Hour | 90-150 KG/Hour |
| LY-40KW | 10000mm1160mm1750mm | ≥40KW | 40KG/Hour | 40KG/Hour | 120-200KG/Hour |
| LY-50KW | 12500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥50KW | 50KG/Hour | 500KG/Hour | 150-250KG/Hour |
| LY-60KW | 13500mm1450mm1750mm | ≥60KW | 60KG/Hour | 600KG/Hour | 180-300KG/Hour |
| LY-70KW | 13500mm1500mm1750mm | ≥70KW | 70KG/Hour | 700KG/Hour | 210-350KG/Hour |
| LY-80KW | 13500mm1650mm1750mm | ≥80KW | 80KG/Hour | 800KG/Hour | 240-400KG/Hour |
| LY-100KW | 16800mm1650mm1750mm | ≥100KW | 100KG/Hour | 1000KG/Hour | 300-500KG/Hour |
| LY-150KW | 22400mm1850mm1750mm | ≥150KW | 150KG/Hour | 1500KG/Hour | 450-750KG/Hour |
| LY-200KW | 27000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥250KW | 250KG/Hour | 2500KG/Hour | 750-1250/Hour |
| LY-300KW | 32000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥300KW | 300KG/Hour | 3000KG/Hour | 900-1500KG/Hour |
| Power Supply | 380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire | ||||
| Microwave Output Frequency | 2450±50Mhz | ||||
| Microwave Input Apparent Power | ≤168Kva | ||||
| Microwave Output Power | ≥120Kw | ||||
| Microwave Power Adjustment Range | 0-30Kw(Adjustable) | ||||
| Ambient Temperature | -5-40°C | ||||
| Relative Humidity | ≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas | ||||
| Transmission Speed | 0-10m/Min(Adjustable) | ||||

Application of microwave sterilizers
In 2024, sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines are at the forefront of food processing technology, offering unparalleled efficiency and effectiveness in preserving the quality and safety of sauces. Let's delve into their application in various industries:
1. Food Industry:
Sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines play a crucial role in the food industry, particularly in the production of sauces, condiments, and dressings. These machines effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms such as bacteria and molds, extending the shelf life of sauces while maintaining their flavor and nutritional value.
2. Catering and Hospitality:
In the catering and hospitality sector, sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines are invaluable for ensuring food safety and quality. Restaurants, hotels, and catering services rely on these machines to sterilize large batches of sauces efficiently, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and enhancing customer satisfaction.
3. Packaging and Distribution:
Before sauces are packaged and distributed to retailers and consumers, they undergo sterilization using tunnel type microwave sterilization machines. This process ensures that the sauces remain safe for consumption throughout their shelf life, even under varying storage conditions. It also minimizes the need for preservatives, making sauces more appealing to health-conscious consumers.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry:
In the pharmaceutical industry, sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines are utilized for the sterilization of medicinal sauces and suspensions. These machines ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products by eliminating harmful pathogens and contaminants, meeting stringent regulatory requirements.
5. Research and Development:
Innovations in sauces tunnel type microwave sterilization machines continue to drive advancements in food processing technology. Research and development efforts focus on enhancing sterilization efficiency, optimizing energy consumption, and improving the overall performance of these machines to meet the evolving needs of the food industry.
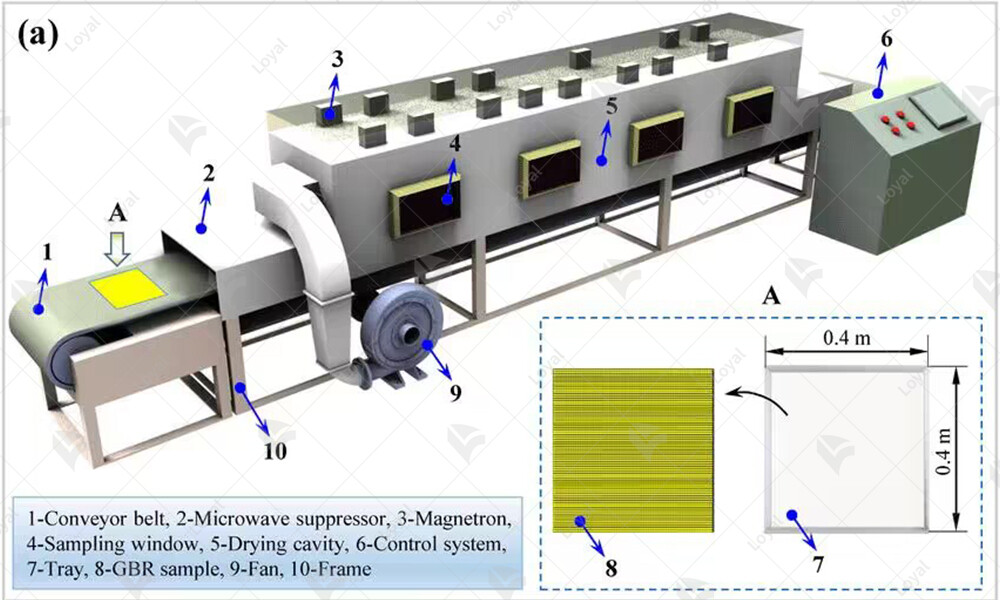
Precautions for selection and implementation of microwave sterilizers
When selecting and implementing microwave sterilizers, there are several key precautions to consider to ensure optimal performance and effectiveness in sterilizing sauces. Here are some essential guidelines to follow:
1. Compatibility with Sauces:
Ensure that the microwave sterilization machine is compatible with the specific characteristics of sauces, including viscosity, consistency, and ingredients. Choose a machine that can accommodate the unique properties of sauces without compromising the sterilization process.
2. Capacity and Throughput:
Consider the production capacity and throughput requirements of your sauce production facility. Select a tunnel type microwave sterilization machine that can handle the volume of sauces produced daily while maintaining efficient processing times.
3. Uniform Heating and Sterilization:
Verify that the microwave sterilization machine provides uniform heating and sterilization throughout the entire batch of sauces. Uneven heating can lead to inconsistent sterilization and potentially unsafe products. Look for machines with advanced heating technology to ensure thorough sterilization.
4. Temperature and Pressure Control:
Ensure that the microwave sterilizer offers precise temperature and pressure control to achieve optimal sterilization conditions for sauces. Control over these parameters is critical for effectively eliminating pathogens and ensuring the safety of the final product.
5. Compliance with Regulations:
Ensure that the microwave sterilization machine complies with relevant food safety regulations and industry standards. This includes adhering to guidelines set forth by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or equivalent authorities in your region.
6. Operator Training and Maintenance:
Provide comprehensive training for operators responsible for operating the microwave sterilization machine. Proper training ensures that operators understand how to safely and effectively use the equipment, reducing the risk of errors or accidents. Additionally, establish a regular maintenance schedule to keep the machine in optimal working condition.
7. Validation and Monitoring:
Implement validation procedures to verify the effectiveness of the microwave sterilization process for sauces. Monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and microbial load to ensure consistent sterilization results. Regularly validate the sterilization process to maintain compliance with food safety standards.
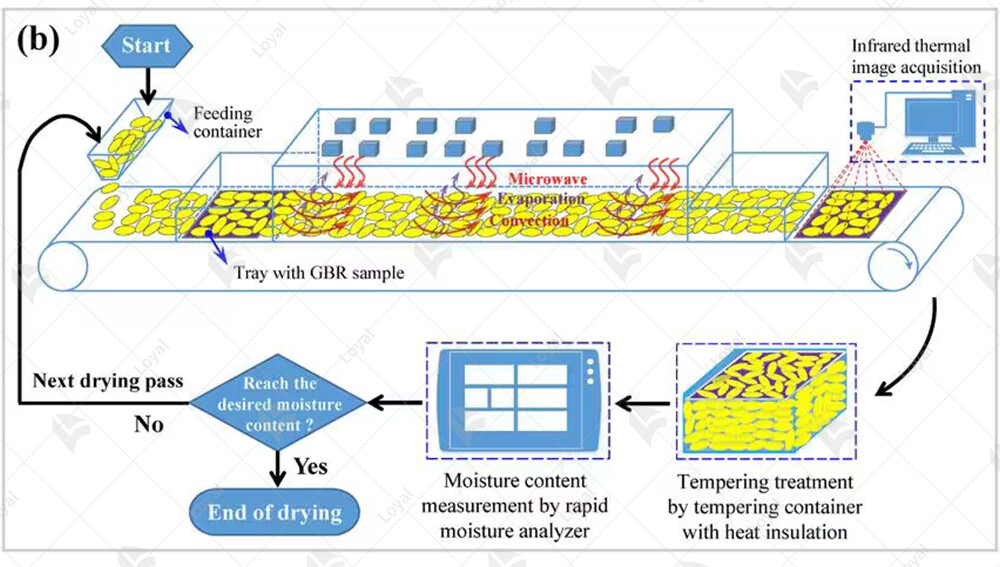
Challenges and limitations of microwave sterilizers
Challenges and limitations are inherent in the operation of microwave sterilizers, particularly when it comes to sauces and other liquid-based products. Despite their effectiveness in eliminating harmful pathogens, microwave sterilization machines face several obstacles that must be addressed for optimal performance.
1. Uneven Heating:
One of the primary challenges of microwave sterilizers is achieving uniform heating, especially with sauces that have varying thickness and viscosity. Microwave energy penetrates unevenly, leading to potential cold spots where sterilization may be inadequate. This can compromise food safety and quality.
2. Limited Penetration Depth:
Microwaves have limited penetration depth, particularly in dense or viscous liquids like sauces. This limitation can result in incomplete sterilization of the inner layers of the product, posing a risk of microbial contamination. It's essential to optimize processing parameters to ensure thorough sterilization throughout the entire volume of the sauce.
3. Sensitivity to Container Material:
The material of the container holding the sauce can influence the effectiveness of microwave sterilization. Certain materials, such as metal or thick plastics, can reflect or absorb microwaves, leading to uneven heating and potential damage to the container. Choosing microwave-compatible packaging materials is critical to ensure uniform sterilization and prevent packaging failures.
4. Overheating and Product Degradation:
Microwave sterilization can sometimes lead to overheating of the sauce, especially if the process parameters are not carefully controlled. Overheating can result in changes to the texture, color, and flavor of the sauce, affecting its overall quality and consumer acceptance. It's essential to monitor the process closely and implement appropriate controls to prevent overheating.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Meeting regulatory requirements for food safety and quality presents a significant challenge for microwave sterilization machines, particularly in the case of sauces. Regulatory authorities often impose strict guidelines for sterilization processes, including validation of microbial reduction and documentation of processing parameters. Ensuring compliance with these regulations requires robust quality assurance protocols and meticulous record-keeping.
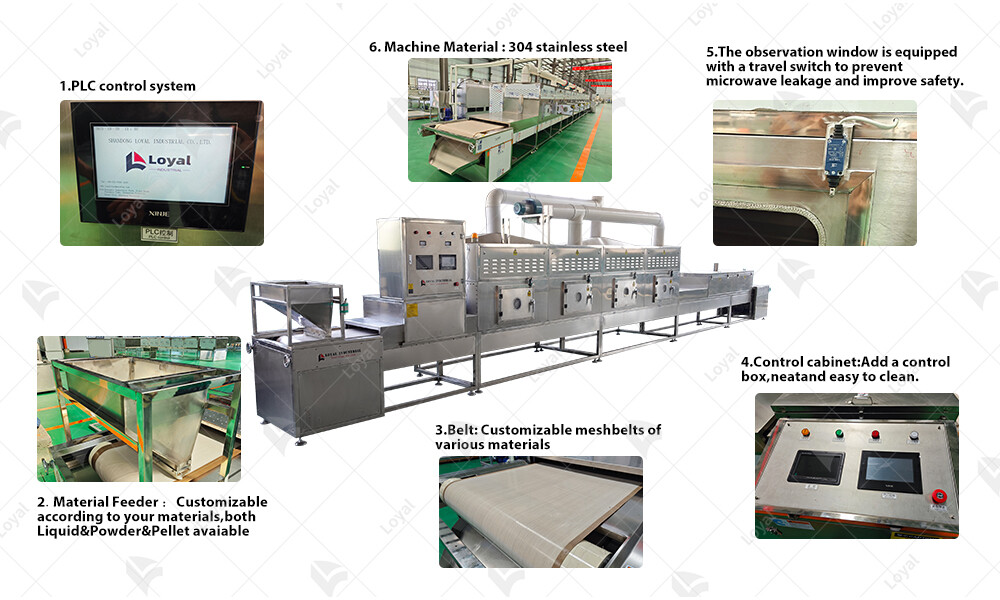

Post-maintenance of microwave sterilizers
Post-maintenance of microwave sterilizers is essential to ensure their continued optimal performance and reliability in the sterilization of sauces. In 2024, as the demand for safe and high-quality sauces continues to rise, it's crucial to implement proper maintenance procedures to uphold food safety standards and preserve product quality.
Cleaning and Sanitization:
One of the primary post-maintenance tasks for microwave sterilizers is thorough cleaning and sanitization. All components of the sterilization machine, including the tunnel, conveyor belts, and heating elements, should be cleaned using approved cleaning agents and methods. This helps remove any food residue, grease, or bacteria that may accumulate during operation.
Inspection of Components:
Regular inspection of the microwave sterilizer's components is essential to identify any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Focus on inspecting seals, gaskets, and electrical connections to ensure they are intact and functioning correctly. Replace any damaged or worn-out parts promptly to prevent leakage or equipment failure.
Calibration and Adjustment:
Calibration of the microwave sterilizer is crucial to ensure consistent and effective sterilization of sauces. Adjust power levels, conveyor speed, and other parameters according to manufacturer specifications to maintain optimal performance. Use calibrated instruments and follow standard procedures to achieve accurate results.
Testing and Validation:
After maintenance procedures are completed, conduct testing and validation to verify the performance of the microwave sterilizer. Run test cycles with controlled parameters and monitor the sterilization process closely. Validate the effectiveness of the sterilization by testing samples of sauces for microbial load and quality attributes.
Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities and testing results. Document cleaning schedules, component inspections, calibration adjustments, and validation tests. Keep comprehensive records to demonstrate compliance with food safety regulations and quality assurance standards.
Training and Education:
Provide training for operators and maintenance personnel on proper post-maintenance procedures for microwave sterilizers. Ensure that staff members are familiar with the operation of the sterilization machine and understand their responsibilities in maintaining its functionality and cleanliness. Continuous education and training are essential for upholding food safety standards and optimizing machine performance.

References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of industrial microwaves:
1. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
Website: [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/]
2.ScienceDirect
Website: [https://www.sciencedirect.com/]
3. SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4. Wiley Online Library
Website: [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/]
5. PubMed
Website: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/]
 Telephone :+86-531-55583139
Telephone :+86-531-55583139 WhatsApp :+86 13256674591
WhatsApp :+86 13256674591 Email :
Email :