Everything you Need to Know About Microwave Drying Sterilizing Oven
Introduction
Microwave drying sterilizing ovens have become an essential tool in the industrial food machinery sector. These advanced devices combine drying and sterilizing processes, offering significant advantages over traditional methods. They are designed to ensure food safety and extend shelf life by effectively eliminating pathogens and reducing moisture content. The use of microwave energy allows for rapid and uniform heating, making these ovens highly efficient and reliable for large-scale food processing operations.
The adoption of microwave drying sterilizing ovens in the food industry has been driven by the need for safer, faster, and more energy-efficient sterilization methods. These ovens are widely used in various food processing applications, including the drying and sterilization of spices, herbs, grains, and ready-to-eat meals. By leveraging microwave technology, manufacturers can achieve superior results in terms of product quality, safety, and cost-effectiveness.

Working Principle of Microwave Sterilizers
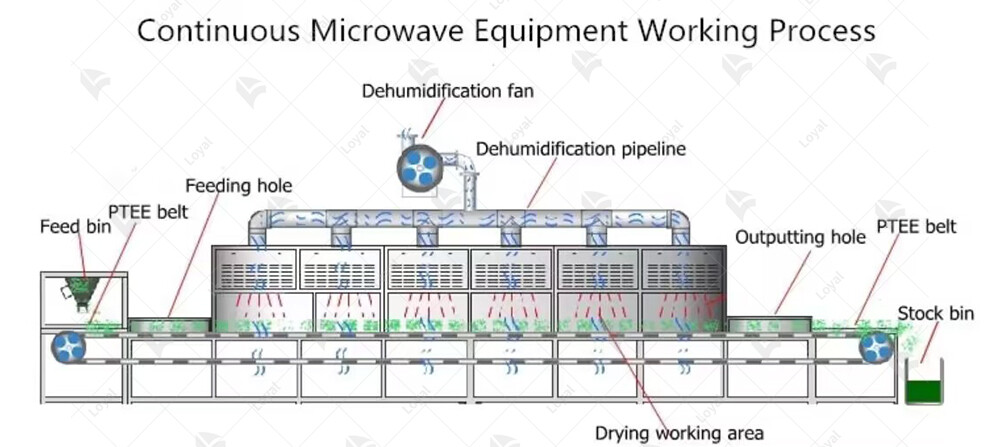
The working principle of microwave drying sterilizing ovens is based on the generation and application of microwave energy. Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with frequencies ranging from 300 MHz to 300 GHz. In industrial applications, the most commonly used frequency is 2450 MHz, which is particularly effective for both drying and sterilizing processes.
When the microwave drying sterilizing oven is activated, the magnetron or solid-state device generates microwaves that penetrate the food product. These microwaves cause polar molecules, primarily water molecules, to oscillate rapidly, generating heat through molecular friction. This heat is distributed evenly throughout the product, ensuring uniform drying and sterilization.
The dual function of drying and sterilizing is achieved by precisely controlling the microwave energy and the environment within the oven. During the drying phase, the moisture content in the food is reduced as the water molecules are heated and evaporated. In the sterilization phase, the high temperatures achieved by the microwaves effectively destroy bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, ensuring the safety and longevity of the food product.
The working principle of microwave drying sterilizing ovens revolves around the efficient use of microwave energy to achieve rapid and uniform drying and sterilization. Their advanced technology and operational efficiency make them a vital component of modern industrial food machinery, ensuring that food products are safe, high-quality, and produced in a cost-effective manner. By integrating microwave drying sterilizing ovens into their processes, food manufacturers can meet the growing demands for safe, shelf-stable products in today's competitive market.

Comparison and Advantages of Microwave Technology and Traditional Sterilization Methods
Feature/Aspect | Microwave Drying Sterilizing Oven | Traditional Sterilization Methods |
| Sterilization Process | Uses microwave radiation to generate heat and destroy microorganisms | Utilizes steam, chemicals, or dry heat for sterilization |
| Time Efficiency | Rapid heating and drying, significantly reducing processing time | Longer processing times due to slower heat penetration |
| Energy Consumption | More energy-efficient due to direct heating | Higher energy consumption due to indirect heating methods |
| Temperature Control | Precise temperature control ensuring consistent results | Temperature control can be less precise |
| Product Quality | Maintains nutritional and sensory qualities of food products | Potential degradation of food quality due to prolonged exposure to heat or chemicals |
| Versatility | Can handle a variety of products, including heat-sensitive items | Limited versatility, especially with heat-sensitive products |
| Environmental Impact | Lower environmental impact due to reduced energy usage and no chemical residues | Higher environmental impact due to higher energy usage and possible chemical disposal issues |
| Installation and Maintenance | Generally easier to install and maintain | Can be complex and costly to install and maintain |
| Initial Investment | Higher initial investment but better long-term cost efficiency | Lower initial investment but higher operational costs |
| Operational Safety | Safe with proper shielding and control measures | Risks associated with handling chemicals or high-pressure steam |

Key Insights:
Efficiency and Speed: The Microwave Drying Sterilizing Oven excels in efficiency and speed. Traditional methods, such as steam or chemical sterilization, require more time due to slower heat transfer. Microwave technology quickly heats and sterilizes products, significantly reducing processing time.
Energy Usage: Microwave Drying Sterilizing Ovens are more energy-efficient. They directly transfer energy to the product, minimizing energy loss. Traditional methods often involve heating water or air first, which consumes more energy.
Quality Preservation: One of the critical advantages of microwave technology is its ability to maintain the nutritional and sensory quality of food products. Traditional methods may lead to nutrient loss or changes in texture and flavor due to prolonged exposure to heat or chemicals.
Environmental Considerations: Microwave sterilization is more environmentally friendly. It uses less energy and does not involve chemicals that could harm the environment. Traditional methods, especially those using chemicals, can have a higher environmental footprint.
Versatility and Safety: Microwave Drying Sterilizing Ovens offer greater versatility, capable of handling various products, including those sensitive to heat. Safety is also enhanced with proper controls, while traditional methods might pose risks with high-pressure steam or chemicals.

Technical Parameters
Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine | |||||
| Model | Size L*W*H(Can be customized according to the customer's requirements) | Output power | Dewaterability | Sterilization capacity | Baking and Roasting capacity (Depends on different raw material) |
| LY-10KW | 5000mm*825mm*1750mm | ≥10KW | 10KG/Hour | 100KG/Hour | 30-50KG/Hour |
| LY-20KW | 8000mm*825mm*1750mm | ≥20KW | 20KG/Hour | 200KG/Hour | 60-100KG/Hour |
| LY-30KW | 8500mm*1160mm*1750mm | ≥30KW | 30KG/Hour | 300KG/Hour | 90-150 KG/Hour |
| LY-40KW | 10000mm*1160mm*1750mm | ≥40KW | 40KG/Hour | 40KG/Hour | 120-200KG/Hour |
| LY-50KW | 12500mm*1160mm*1750mm | ≥50KW | 50KG/Hour | 500KG/Hour | 150-250KG/Hour |
| LY-60KW | 13500mm*1450mm*1750mm | ≥60KW | 60KG/Hour | 600KG/Hour | 180-300KG/Hour |
| LY-70KW | 13500mm*1500mm*1750mm | ≥70KW | 70KG/Hour | 700KG/Hour | 210-350KG/Hour |
| LY-80KW | 13500mm*1650mm*1750mm | ≥80KW | 80KG/Hour | 800KG/Hour | 240-400KG/Hour |
| LY-100KW | 16800mm*1650mm*1750mm | ≥100KW | 100KG/Hour | 1000KG/Hour | 300-500KG/Hour |
| LY-150KW | 22400mm*1850mm*1750mm | ≥150KW | 150KG/Hour | 1500KG/Hour | 450-750KG/Hour |
| LY-200KW | 27000mm*1850mm*1750mm | ≥250KW | 250KG/Hour | 2500KG/Hour | 750-1250/Hour |
| LY-300KW | 32000mm*1850mm*1750mm | ≥300KW | 300KG/Hour | 3000KG/Hour | 900-1500KG/Hour |
Power Supply | 380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire | ||||
Microwave Output Frequency | 2450±50Mhz | ||||
Microwave Input Apparent Power | ≤168Kva | ||||
Microwave Output Power | ≥120Kw | ||||
Microwave Power Adjustment Range | 0-30Kw(Adjustable) | ||||
Ambient Temperature | -5-40°C | ||||
Relative Humidity | ≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas | ||||
Transmission Speed | 0-10m/Min(Adjustable) | ||||
Application of Microwave Sterilizers
Application Area | Description |
| Food Industry | Microwave sterilizers are extensively used in the food industry for sterilizing various food products such as meat, vegetables, and ready-to-eat meals, ensuring microbial safety and prolonging shelf life. |
| Pharmaceuticals | In pharmaceutical manufacturing, microwave sterilizers play a crucial role in ensuring the sterility of medicines, medical instruments, and packaging materials, complying with stringent regulatory standards and reducing contamination risks. |
| Laboratory Settings | Microwave sterilizers are commonly employed in laboratory settings for sterilizing laboratory equipment, glassware, and media, providing rapid and effective sterilization for research and experimental purposes. |
| Healthcare Facilities | Microwave sterilizers find applications in healthcare facilities for sterilizing medical instruments, surgical equipment, and dressings, contributing to infection control and patient safety in hospitals and clinics. |

Technological Progress and Innovation of Microwave Sterilizers
Advanced Control Systems: Modern microwave sterilizers are equipped with advanced control systems that allow precise adjustment of sterilization parameters such as temperature, humidity, and exposure time, optimizing sterilization effectiveness.
Integration of IoT: The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology enables remote monitoring and control of microwave sterilizers, facilitating real-time tracking of sterilization processes and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Ongoing technological advancements have led to the development of energy-efficient microwave sterilizers that minimize energy consumption while maintaining high sterilization efficacy, reducing operational costs for users.
Innovative Sterilization Techniques: Manufacturers are continuously innovating sterilization techniques, such as combining microwave sterilization with other technologies like UV-C irradiation or ozone treatment, to achieve synergistic sterilization effects and enhance microbial inactivation rates.

Precautions for Selection and Implementation of Microwave Sterilizers
Precaution | Description |
| Power Requirements | Ensure the oven's power requirements align with the facility's electrical capacity. |
| Material Compatibility | Verify that materials used in the oven construction are food-grade and compatible with microwave radiation. |
| Capacity Consideration | Select an oven size that matches the production volume to avoid underutilization or overloading. |
| Safety Features | Prioritize ovens equipped with safety features such as interlocks to prevent accidental exposure to microwave radiation. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Confirm that the oven meets relevant industry standards and regulations for food processing equipment. |
| Installation Expertise | Engage qualified professionals for the installation to ensure proper setup and functionality. |
| Operator Training | Provide comprehensive training for operators to handle the oven safely and effectively. |
| Maintenance Plan | Develop a routine maintenance plan to keep the oven in optimal condition and prevent breakdowns. |

Challenges and Limitations of Microwave Sterilizers
Challenge / Limitation | Description |
| Uneven Heating | Microwave radiation may result in uneven heating, requiring careful positioning of products within the oven. |
| Material Constraints | Certain materials, such as metal, may reflect microwave radiation, limiting their use in microwave sterilizers. |
| Temperature Control | Maintaining precise temperature control can be challenging in microwave sterilizers, affecting the quality of the sterilization process. |
| Moisture Content | Products with high moisture content may require longer processing times in microwave sterilizers, impacting efficiency. |
| Energy Consumption | Microwave sterilizers can consume significant amounts of energy, leading to higher operational costs. |
| Limited Penetration | Microwave radiation has limited penetration depth, potentially leaving some areas of thicker products under-sterilized. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting stringent regulatory requirements for microwave sterilization processes can be complex and time-consuming. |
| Operator Skill Requirement | Operating microwave sterilizers effectively may require specialized training and expertise. |
| Adaptation for Different Products | Adapting microwave sterilizers for different product types may require adjustments to parameters and processes. |
| Maintenance Challenges | Maintenance of microwave sterilizers, especially components exposed to high levels of radiation, can pose logistical and safety challenges. |

Impact of Microwave Sterilizers on the Environment
Microwave drying sterilizing ovens offer several environmental benefits compared to traditional sterilization methods. One significant advantage is their energy efficiency. By utilizing microwaves to heat and sterilize products, these ovens consume less energy compared to conventional methods such as steam sterilization or chemical treatments. This reduced energy consumption translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions and overall environmental impact.
Additionally, microwave sterilizers typically have shorter processing times compared to traditional methods. This not only increases productivity but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with the sterilization process. Shorter processing times mean less energy consumption and fewer resources required to complete the sterilization cycle.
Furthermore, microwave sterilization eliminates the need for harmful chemicals or additives that are often used in conventional sterilization processes. This reduces the release of pollutants into the environment and minimizes the risk of contamination of soil, water, and air.
In summary, microwave drying sterilizing ovens offer a more environmentally friendly sterilization solution by reducing energy consumption, minimizing processing times, and eliminating the use of harmful chemicals.

Future Trends in Microwave Sterilizer Technology
The future of microwave sterilizer technology is poised for significant advancements driven by ongoing research and development efforts. One of the key areas of focus is improving the efficiency and effectiveness of microwave sterilization processes.
Researchers are exploring ways to enhance the uniformity of microwave heating within the sterilizing chamber to ensure thorough and consistent sterilization of products. This may involve the development of advanced heating systems and innovative chamber designs that optimize microwave distribution.
Another area of innovation is the integration of smart technologies into microwave sterilizers. These technologies may include IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities for remote monitoring and control, predictive maintenance algorithms to anticipate equipment failures, and real-time data analytics for process optimization.
Furthermore, there is growing interest in the development of microwave sterilizers that are specifically tailored to the needs of different industries, such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing. Customized sterilization solutions may include modular designs, adjustable power settings, and specialized sensors to accommodate a wide range of products and production requirements.
Overall, the future of microwave sterilizer technology holds promise for advancements in efficiency, effectiveness, and versatility, paving the way for safer and more sustainable sterilization practices across various industries.

Conclusion
Microwave drying sterilizing ovens demonstrate clear environmental benefits, notably through their energy efficiency, reduced processing times, and elimination of harmful chemicals. These ovens offer a more sustainable sterilization solution compared to traditional methods, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing environmental pollution.
Looking ahead, the future of microwave sterilizer technology holds exciting possibilities with ongoing advancements aimed at enhancing efficiency, effectiveness, and versatility. Smart technologies, improved heating systems, and customized solutions tailored to different industries are driving innovation in this field, promising safer and more sustainable sterilization practices in the years to come.

References
1. Website: Food Processing Technology
URL: https://www.foodprocessing-technology.com/
2. Website: Food Engineering Magazine
URL: https://www.foodengineeringmag.com/
3. Website: Food Manufacturing Magazine
URL: https://www.foodmanufacturing.com/
4. Website: Packaging Digest
URL: https://www.packagingdigest.com/
5. Website: Food Quality & Safety Magazine
 Telephone :+86-531-55583139
Telephone :+86-531-55583139 WhatsApp :+86 13256674591
WhatsApp :+86 13256674591 Email :
Email :